Radon, a colorless and odorless radioactive gas, poses a significant health risk when it accumulates indoors. Emerging from the natural decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water, radon can seep into buildings through cracks in foundations, gaps around pipes, and other entry points. Proactive testing for radon levels is paramount in safeguarding indoor air quality and minimizing associated health risks. Through routine testing, homeowners can gain insight into their indoor radon concentrations, allowing for early detection and subsequent mitigation measures if necessary. The first step in addressing radon concerns is comprehensive testing. Short-term tests, lasting anywhere from a few days to several months, provide initial assessments of radon levels within a home. Long-term tests, conducted over duration of more than three months, offer a more accurate depiction of average radon concentrations over time. By employing both short-term and long-term testing strategies, homeowners can obtain a comprehensive understanding of their radon exposure. Additionally, periodic retesting ensures ongoing monitoring and enables timely intervention should radon levels fluctuate.
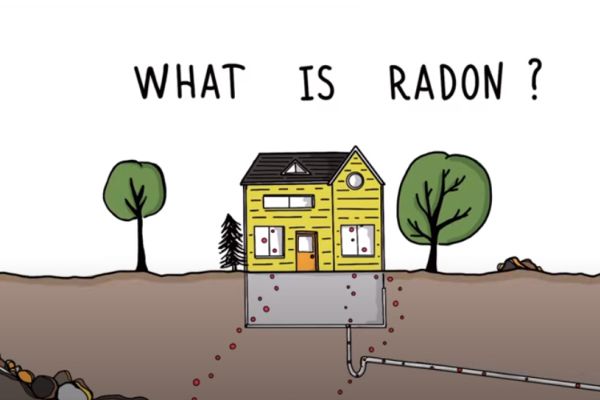
In the event that elevated radon concentrations are detected, proactive mitigation measures become essential. Radon mitigation techniques aim to reduce indoor radon levels, thereby minimizing associated health risks. Common mitigation strategies include sub-slab depressurization, which involves installing a ventilation system to draw radon-laden air from beneath the foundation and vent it safely outdoors. Other approaches may include sealing cracks and gaps in the foundation, improving ventilation in crawl spaces, and installing radon-reducing barriers. Collaboration with qualified radon mitigation professionals is crucial in implementing effective mitigation measures. These specialists possess the expertise and resources necessary to assess radon levels accurately and devise tailored mitigation solutions based on the unique characteristics of each property. Moreover, they adhere to established protocols and standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of mitigation efforts. Beyond individual residences, proactive radon testing and mitigation efforts extend to commercial buildings, schools, and other public facilities.
Implementing radon-resistant construction techniques during the building process can help prevent radon infiltration from the outset. Such measures may include installing vapor barriers, using radon-resistant building materials, and incorporating passive ventilation systems. Regular testing and maintenance further support ongoing radon management in these environments. Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives play a pivotal role in fostering proactive radon testing and mitigation practices. By disseminating information about the risks of radon exposure and the importance of testing, communities can empower individuals to take proactive measures to protect their health. Government agencies, public health organizations, and advocacy groups often collaborate to promote radon awareness provide resources for testing mitigation and check that https://www.cleanvapor.com/commercialradon/ for full details. Addressing radon concerns through proactive testing and mitigation measures is paramount for safeguarding indoor air quality and protecting public health. By conducting routine testing, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and raising awareness within communities, individuals and organizations can mitigate the risks associated with radon exposure and create safer indoor environments for all.
